Listen up, folks. Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne illness that affects millions of people each year, especially in tropical and subtropical regions. This disease, caused by the dengue virus, is serious business and poses significant health risks. It’s crucial for all of us to understand its symptoms, prevention methods, and treatment options if we want to keep ourselves and our communities safe.
Here’s the deal: dengue fever has become a growing concern in recent years. It’s spreading faster than ever, and the number of cases is skyrocketing. The Aedes aegypti mosquito, the primary culprit behind this illness, is responsible for transmitting the virus through its bite. This article is your go-to guide for everything dengue fever. We’re going to break it down for you, step by step, so you can be fully equipped with the knowledge to prevent and manage this potentially life-threatening condition.
As we dive deeper into this topic, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of dengue fever. But that’s not all—we’ll also talk about prevention strategies and ways to stop the spread of this dangerous illness. By the time you finish reading, you’ll have a clearer understanding of how to protect yourself and your loved ones. Let’s get started.
Read also:T33nleaks The Inside Scoop On The Latest Tech Whistleblowing Phenomenon
Table of Contents
- What is Dengue Fever?
- Causes of Dengue Fever
- Symptoms of Dengue Fever
- Diagnosis of Dengue Fever
- Treatment Options
- Prevention Methods
- Dengue Fever Statistics
- Global Impact of Dengue Fever
- Research and Development
- Conclusion
What is Dengue Fever?
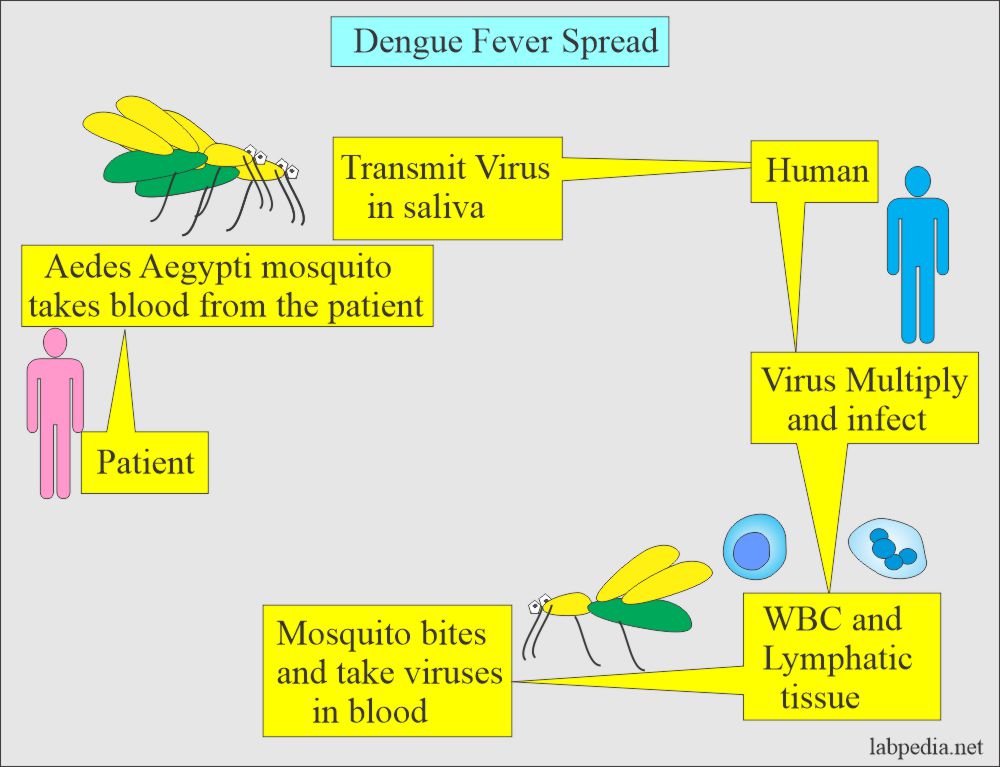
Dengue fever is a viral infection spread by mosquitoes, primarily the Aedes aegypti species. Think of it like this: you’ve got a mosquito buzzing around, and if it’s infected with the dengue virus, one bite can send your body into a world of trouble. The symptoms often mimic the flu, but they’re more intense—high fever, severe headaches, pain behind the eyes, joint and muscle pain, and even a rash. In the worst-case scenarios, it can escalate to dengue hemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome, both of which can be fatal if not treated right away.
This disease thrives in urban and semi-urban areas of tropical and subtropical regions. Countries like Southeast Asia, the Pacific Islands, the Caribbean, Central and South America, and parts of Africa are hotspots for dengue fever. Here’s the kicker: there are four distinct serotypes of the virus. So, if you recover from one type, you’re only immune to that specific serotype. That means you’re still vulnerable to the other three. Talk about tricky.
Key Facts About Dengue Fever
- Dengue fever is caused by the dengue virus, which is transmitted by the Aedes aegypti mosquito.
- It affects millions of people globally, with estimates ranging from 100 to 400 million infections annually.
- In severe cases, it can lead to life-threatening complications, such as dengue hemorrhagic fever.
Causes of Dengue Fever
The root cause of dengue fever is the dengue virus, which belongs to the Flavivirus genus. Here’s how it works: an infected Aedes aegypti mosquito bites a person, and the virus enters their bloodstream. These mosquitoes love to breed in stagnant water and are most active during the early morning and late afternoon. Once bitten, the virus spreads through the bloodstream, leading to infection.
But the cycle doesn’t stop there. When the mosquito bites another person after feeding on someone infected, it spreads the virus further. This is why densely populated areas are particularly vulnerable to rapid outbreaks. Urbanization, inadequate waste management, and climate change all contribute to the perfect storm for dengue fever to thrive.
Factors Contributing to the Spread of Dengue Fever
- Urbanization and poor waste management leading to stagnant water accumulation—basically, mosquito breeding heaven.
- Climate change extending the breeding season for mosquitoes, giving them more time to wreak havoc.
- Increased international travel and migration, making it easier for the virus to hop borders.
Symptoms of Dengue Fever
Now, let’s talk about what happens when you’re bitten by an infected mosquito. Symptoms usually show up 4 to 10 days after the bite. It starts with a sudden high fever, often accompanied by other flu-like symptoms. Picture this: you’ve got a fever that could hit up to 104°F (40°C), a pounding headache, pain behind the eyes, muscle and joint pain so bad it’s sometimes called "breakbone fever," nausea, vomiting, and a rash. Not fun, right?
In severe cases, things can get much worse. The fever might progress to dengue hemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome. These conditions involve bleeding, dangerously low platelet counts, and circulatory collapse. If you or someone you know experiences these symptoms, it’s critical to seek medical attention immediately. Time is of the essence here.
Read also:Michael Schoeffling The Rising Star In The World Of Business And Beyond
Diagnosis of Dengue Fever
Diagnosing dengue fever isn’t as simple as taking your temperature. Healthcare providers rely on a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. They’ll ask about your symptoms, travel history, and exposure to mosquitoes. Then, they’ll run blood tests to detect the presence of the dengue virus or antibodies against it.
Here’s a breakdown of the common diagnostic tests:
Types of Laboratory Tests
- NS1 antigen test: This test detects the presence of the dengue virus in the early stages of infection. It’s like catching the thief red-handed.
- IgM and IgG antibody tests: These identify antibodies your body produces in response to the virus. Think of them as your body’s defense team.
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction) test: This test detects the genetic material of the virus, confirming the diagnosis. It’s like DNA evidence in a crime scene investigation.
Treatment Options
Here’s the tough part: there’s no specific medication to treat dengue fever. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications. If you’re diagnosed, your doctor will likely advise you to rest, stay hydrated, and take over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen to reduce fever and pain. But here’s a warning: avoid aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) because they can increase the risk of bleeding.
In severe cases, hospitalization might be necessary. Doctors will closely monitor your condition and provide supportive care, which could include intravenous fluids and blood transfusions if needed. Early recognition and prompt medical intervention are key to managing severe dengue fever. Don’t wait—act fast.
Prevention Methods
Preventing dengue fever is all about controlling the mosquito population and avoiding mosquito bites. It’s like playing defense in a game of dodgeball. You want to avoid getting hit, right? Here’s how you can do it:
Personal Protective Measures
- Use mosquito repellents containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus. These are your first line of defense.
- Wear long-sleeved clothing and pants to minimize exposed skin. Think of it as wearing armor against those pesky mosquitoes.
- Sleep under mosquito nets, especially in high-risk areas. It’s like putting up a shield around your bed.
Environmental Control Measures
- Eliminate standing water sources where mosquitoes can breed. This includes flower pots, old tires, and even bottle caps. Every little bit helps.
- Cover water storage containers and properly dispose of waste. It’s like cleaning up the neighborhood to keep it safe.
- Support community-wide mosquito control programs, such as fogging and larviciding. These efforts can make a big difference in reducing mosquito populations.
Dengue Fever Statistics
Dengue fever is a major global health issue. Here’s the reality: there are an estimated 100 to 400 million infections each year. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), about 500,000 people end up in the hospital annually due to severe dengue, with many fatalities in some regions. The numbers are staggering.
Over the past few decades, the incidence of dengue fever has exploded. Since the 1960s, cases have increased 30-fold. Why? Urbanization, climate change, and increased global travel are all contributing factors. It’s a complex problem that requires a coordinated response.
Global Impact of Dengue Fever
The impact of dengue fever goes beyond health—it affects economies and societies as well. The economic burden includes healthcare costs, lost productivity, and expenses related to mosquito control programs. Developing countries, in particular, face significant challenges due to limited resources and infrastructure.
Fighting dengue fever requires teamwork at local, national, and international levels. Public health initiatives, such as education campaigns and research into new vaccines and treatments, are essential. It’s a battle we can win, but it’ll take all of us working together.
Research and Development
Research into dengue fever is making strides, with a focus on developing effective vaccines and treatments. One example is the CYD-TDV (Dengvaxia) vaccine, which has shown promise in reducing severe dengue cases and hospitalizations. However, there are still challenges to ensure the vaccine is safe and effective for everyone.
Emerging technologies, like genetically modified mosquitoes and Wolbachia bacteria, are offering innovative ways to control mosquito populations and reduce dengue transmission. Continued investment in research and development is critical. We’re on the right track, but there’s still work to be done.
Conclusion
Dengue fever is a serious global health concern that demands our attention and action. By understanding its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment, we can take proactive steps to prevent and manage this illness. Implementing effective prevention strategies and supporting ongoing research efforts are crucial to reducing its impact worldwide.
So, here’s what I’m asking you to do: share this article and spread awareness about dengue fever. The more people know, the better equipped we are to fight it. Together, we can work towards a future where the threat of dengue fever is minimized, ensuring healthier and safer communities for all. For more information on dengue fever and other health topics, explore our website and stay informed.