Burns are one of the most common injuries worldwide, and understanding burn degrees is crucial for proper treatment and care. Whether it’s a minor kitchen mishap or a more severe accident, recognizing the severity of burns can make a significant difference in recovery outcomes. In this article, we will explore the various levels of burn injuries, their symptoms, and the appropriate treatment methods.
Burns can range from minor discomfort to life-threatening conditions. Knowing how to identify the degree of a burn can help you take the necessary steps to ensure safety and healing. Whether you're a healthcare professional or an individual looking to learn more about burn care, this guide will provide detailed insights into the classification of burns.
Our focus will be on explaining the different burn degrees, offering actionable advice, and ensuring that you understand the importance of proper care. Let's dive into the details of each burn degree and how you can recognize and manage them effectively.
Read also:Tesla Model X Interior A Comprehensive Guide To Luxury And Innovation
Table of Contents
- Biography (If Relevant)
- What Are Burn Degrees?
- First-Degree Burns
- Second-Degree Burns
- Third-Degree Burns
- Fourth-Degree Burns
- Symptoms of Burns
- Treatment Options
- Prevention Tips
- Statistics and Data
- Conclusion
What Are Burn Degrees?
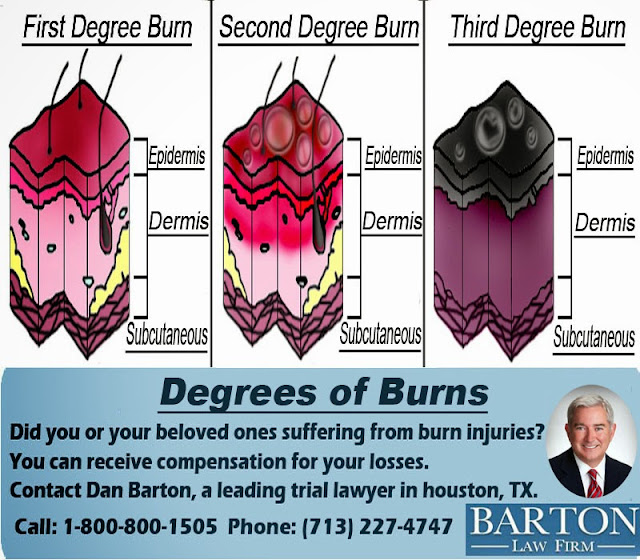
Burn degrees refer to the classification of burns based on the severity and depth of tissue damage. Understanding burn degrees is essential for determining the appropriate treatment and predicting the healing process. Burns are categorized into four primary degrees, each indicating a different level of tissue injury.
Each degree of burn affects different layers of the skin, from the outermost layer (epidermis) to deeper tissues, including muscles and bones. Proper identification of burn degrees ensures timely medical intervention and minimizes complications.
First-Degree Burns
Characteristics and Symptoms
First-degree burns affect only the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. They are typically caused by brief exposure to heat, sunburn, or mild scalds. The symptoms of first-degree burns include:
- Redness
- Pain
- Swelling
- No blisters
These burns usually heal within a week without scarring, but proper care is necessary to prevent infection.
Second-Degree Burns
Depth and Effects
Second-degree burns penetrate deeper into the skin, affecting both the epidermis and the dermis. These burns are often caused by prolonged exposure to heat, chemicals, or severe sunburn. Symptoms include:
- Severe redness
- Pain and swelling
- Blister formation
- Moist appearance
Second-degree burns can take two to three weeks to heal and may leave scars if not treated properly. Medical attention is recommended for extensive burns or burns on sensitive areas like the face, hands, or feet.
Read also:Who Owns Shaw Industries A Comprehensive Exploration Of Ownership History And Influence
Third-Degree Burns
Severe Tissue Damage
Third-degree burns destroy both the epidermis and dermis, extending into the subcutaneous tissue. These burns are often caused by severe heat, flames, or electrical injuries. Symptoms include:
- Charred or white skin
- Lack of sensation due to nerve damage
- Leathery texture
Third-degree burns require immediate medical attention and may necessitate skin grafts or other surgical interventions. Healing can take months, and scarring is almost inevitable.
Fourth-Degree Burns
Life-Threatening Burns
Fourth-degree burns penetrate through all layers of the skin and affect underlying tissues, including muscles, tendons, and bones. These burns are the most severe and can be life-threatening. Symptoms include:
- Blackened or charred skin
- Exposed bone or muscle
- Severe pain or numbness
Fourth-degree burns require emergency medical care and may involve extensive reconstructive surgery and rehabilitation. Recovery can be prolonged and challenging.
Symptoms of Burns
Recognizing the symptoms of burns is crucial for determining the appropriate course of action. Symptoms vary depending on the degree of the burn and may include:
- Redness and swelling
- Pain or numbness
- Blister formation
- Leathery or charred skin
- Moist or dry appearance
It is important to assess the size and location of the burn, as well as any accompanying symptoms, to determine the need for medical intervention.
Treatment Options
First-Degree Burns
Treatment for first-degree burns typically involves:
- Cooling the burn with lukewarm water
- Applying a soothing cream or aloe vera
- Using over-the-counter pain relievers
Second-Degree Burns
Second-degree burns may require:
- Covering the burn with a sterile bandage
- Using antibiotic ointments to prevent infection
- Seeking medical attention for large or deep burns
Third and Fourth-Degree Burns
For severe burns, immediate medical care is essential. Treatment options include:
- Skin grafts
- Antibiotics to prevent infection
- Pain management
- Surgical interventions
Severe burns often require hospitalization and specialized care to ensure proper healing and minimize complications.
Prevention Tips
Preventing burns is key to avoiding injury and ensuring safety. Here are some tips to reduce the risk of burns:
- Keep flammable materials away from heat sources
- Use caution when handling hot liquids or appliances
- Install smoke detectors and fire extinguishers
- Teach children about fire safety
- Wear protective gear when working with chemicals or electricity
By following these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of burn injuries.
Statistics and Data
Burn injuries are a significant global health concern. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), burns account for approximately 180,000 deaths annually worldwide. The majority of these deaths occur in low- and middle-income countries, where access to proper medical care may be limited.
In the United States, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) reports that burns are one of the leading causes of unintentional injury. Approximately 486,000 people receive medical treatment for burn injuries each year, highlighting the importance of education and prevention.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding burn degrees is essential for recognizing the severity of burns and ensuring appropriate treatment. From first-degree burns to life-threatening fourth-degree burns, each level requires different care and attention. By educating ourselves about burn prevention and treatment, we can reduce the risk of injury and improve recovery outcomes.
We encourage you to share this article with others to spread awareness about burn safety. If you have any questions or experiences to share, please leave a comment below. Additionally, explore our other articles for more information on health and safety topics.