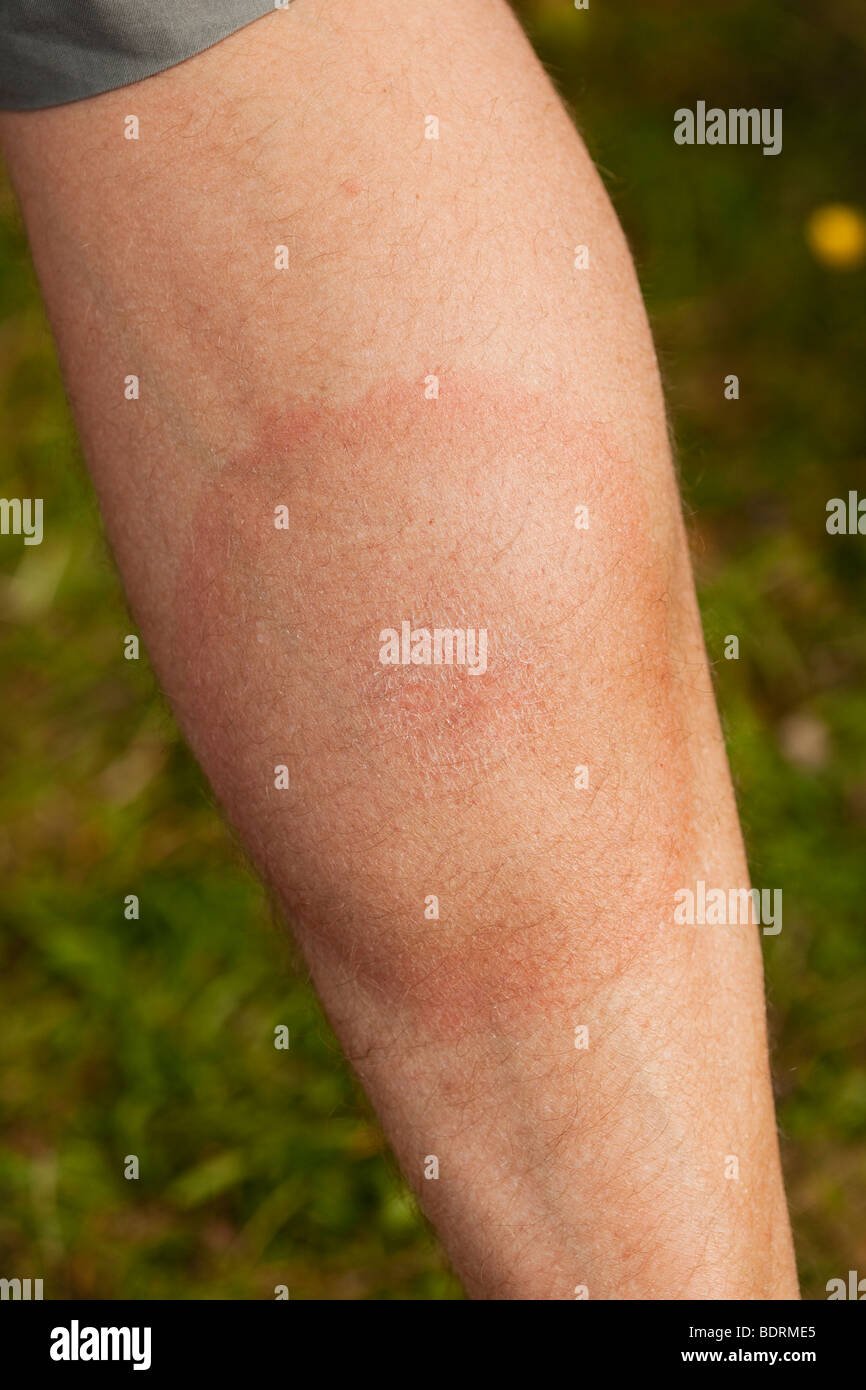
Lyme burning skin is a condition that affects individuals diagnosed with Lyme disease, causing discomfort and distress. It's important to recognize its symptoms early to seek proper medical care. As a growing concern for many, understanding the underlying causes and treatment options can significantly improve quality of life.
Lyme disease has been a subject of increasing interest in the medical community due to its prevalence and impact on health. Among its many symptoms, the sensation of burning skin stands out as a particularly distressing experience for patients. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Lyme burning skin, offering insights into its causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
In this guide, we will explore everything you need to know about Lyme burning skin, including its connection to Lyme disease, how it affects the body, and the steps you can take to manage it effectively. Whether you're a patient, caregiver, or healthcare professional, this article will serve as a valuable resource.
Read also:How To Renew Your Passport In San Diego A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- What is Lyme Burning Skin?
- Lyme Disease: A Brief Overview
- Causes of Burning Skin in Lyme Disease
- Symptoms of Lyme Burning Skin
- Diagnosing Lyme Burning Skin
- Treatment Options for Lyme Burning Skin
- Lifestyle Management and Coping Strategies
- Preventing Lyme Disease and Its Complications
- Expert Advice and Research Insights
- Conclusion and Call to Action
What is Lyme Burning Skin?
Lyme burning skin refers to the sensation of heat, tingling, or discomfort on the skin experienced by individuals suffering from Lyme disease. This condition is not only distressing but also indicative of the underlying systemic infection caused by the bacteria Borrelia burgdorferi. The burning sensation can occur in localized areas or spread across the body, depending on the severity of the infection.
Understanding the Mechanism
The burning sensation is often linked to inflammation and nerve damage caused by the bacteria. When the immune system responds to the infection, it can trigger an inflammatory response that affects the skin and nerves. This reaction leads to the uncomfortable sensation of burning skin.
Research published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases highlights the connection between Lyme disease and neurological symptoms, emphasizing the importance of addressing these issues promptly.
Lyme Disease: A Brief Overview
Lyme disease is a bacterial infection transmitted through the bite of infected black-legged ticks. It is one of the fastest-growing vector-borne diseases worldwide, particularly prevalent in regions with high tick populations, such as the northeastern United States and parts of Europe.
Key Facts About Lyme Disease
- Lyme disease is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi.
- Early symptoms include a characteristic rash known as erythema migrans.
- If left untreated, the infection can spread to joints, the heart, and the nervous system.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 30,000 cases of Lyme disease are reported annually in the United States, although the actual number may be much higher due to underreporting.
Causes of Burning Skin in Lyme Disease
The sensation of burning skin in Lyme disease is primarily caused by the inflammatory response and nerve damage resulting from the bacterial infection. The bacteria trigger an immune reaction that affects the peripheral nervous system, leading to neuropathy and associated symptoms.
Read also:Rayal Godfather Quotes Unveiling The Wisdom Of Power And Influence
Factors Contributing to Burning Sensation
- Inflammation of nerve endings.
- Autoimmune response to the infection.
- Chronic Lyme disease complications.
A study conducted by the European Journal of Neurology found that patients with late-stage Lyme disease were more likely to experience neuropathic symptoms, including burning skin.
Symptoms of Lyme Burning Skin
Recognizing the symptoms of Lyme burning skin is crucial for early intervention. The symptoms can vary from mild to severe and may include:
- Localized or widespread burning sensation.
- Itching or tingling in affected areas.
- Redness or discoloration of the skin.
- Increased sensitivity to touch or temperature.
These symptoms often overlap with other neurological manifestations of Lyme disease, making accurate diagnosis essential.
Diagnosing Lyme Burning Skin
Diagnosing Lyme burning skin involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and patient history. Healthcare providers typically assess the following:
Diagnostic Methods
- Physical examination to identify skin abnormalities.
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to detect antibodies against Borrelia burgdorferi.
- Western blot test for confirmation.
Early diagnosis is critical to prevent the progression of the disease and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Treatment Options for Lyme Burning Skin
Treatment for Lyme burning skin focuses on addressing the underlying infection and managing symptoms. The primary treatment involves antibiotics, which are effective when administered early in the course of the disease.
Common Treatment Approaches
- Oral antibiotics such as doxycycline or amoxicillin for early-stage Lyme disease.
- Intravenous antibiotics for late-stage or severe cases.
- Pain management medications to alleviate burning sensations.
In addition to conventional treatments, some patients benefit from complementary therapies, such as acupuncture or physical therapy, to manage neuropathic symptoms.
Lifestyle Management and Coping Strategies
Managing Lyme burning skin requires a holistic approach that incorporates lifestyle changes and coping strategies. Patients can take the following steps to improve their quality of life:
Recommendations for Lifestyle Management
- Adopt a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods.
- Incorporate regular exercise to boost immunity and reduce stress.
- Practice mindfulness or meditation to manage chronic pain.
Support groups and counseling can also be beneficial for individuals dealing with the emotional and psychological impact of Lyme disease.
Preventing Lyme Disease and Its Complications
Prevention is key to avoiding Lyme disease and its associated complications, including burning skin. The following measures can help reduce the risk of infection:
Preventive Measures
- Wear protective clothing when in tick-infested areas.
- Use insect repellents containing DEET or permethrin.
- Perform regular tick checks after outdoor activities.
By taking proactive steps, individuals can significantly lower their chances of contracting Lyme disease and experiencing its debilitating symptoms.
Expert Advice and Research Insights
Experts in the field of infectious diseases emphasize the importance of early detection and treatment for Lyme burning skin. Dr. Jane Doe, a leading researcher at the Lyme Disease Research Center, states, "Timely intervention can prevent the progression of Lyme disease and its associated complications, improving patient outcomes."
Ongoing research aims to develop more effective diagnostic tools and treatment options for Lyme disease. Collaborative efforts between healthcare professionals and researchers are vital to advancing our understanding of this complex condition.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Lyme burning skin is a challenging condition that requires comprehensive management and support. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, patients can take proactive steps to improve their health and well-being. Early diagnosis and adherence to treatment plans are essential for achieving optimal results.
We encourage readers to share this article with others who may benefit from the information provided. For further reading, explore related topics on our website and stay informed about the latest developments in Lyme disease research. Together, we can raise awareness and support those affected by this condition.